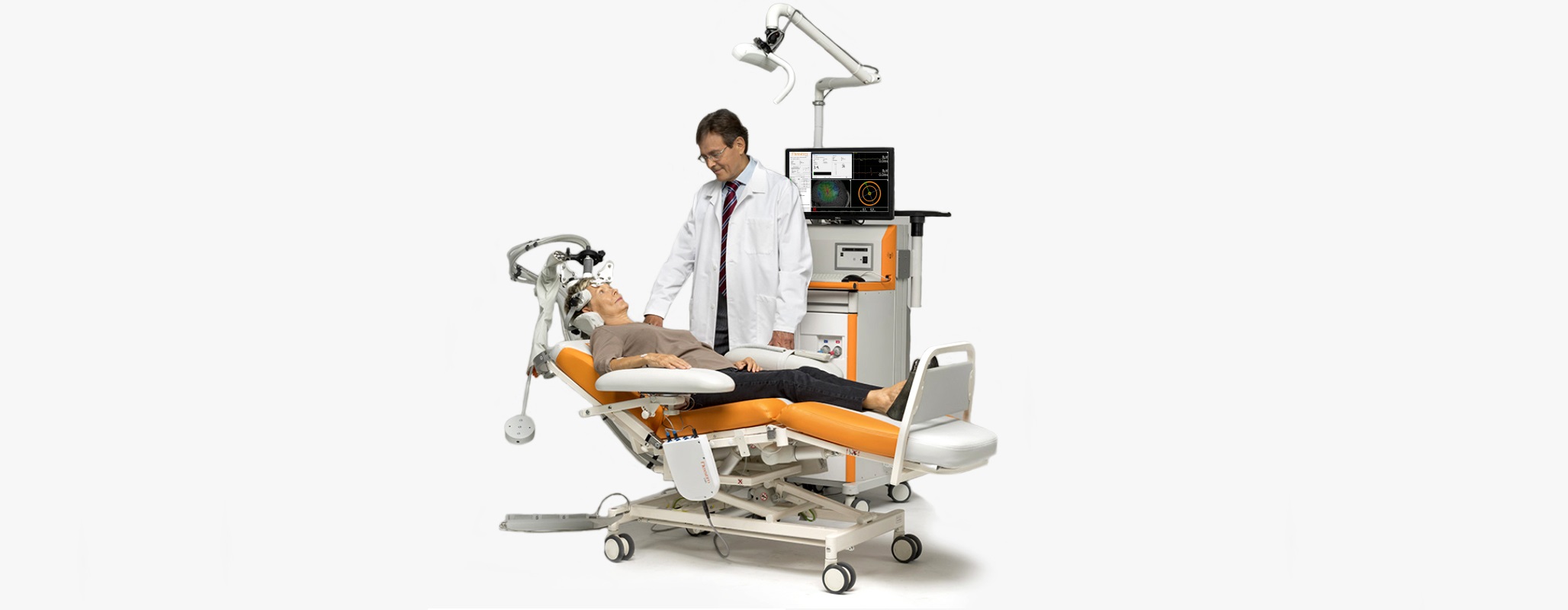
The first and the only navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation device (SmartFocus™TMS 智能聚焦腦磁激) approved by FDA for depression (抑鬱症).
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) stimulates the brain using small electrical fields in essence, not magnetic fields. A coil resting against the patient’s head communicates directly with the underlying neurons of the brain. The Nexstim Navigated Brain Therapy (NBT®) System uses TMS with sophisticated navigation tools to visualize the location, orientation and magnitude of the maximum stimulating electric-field (E-field) induced when the TMS coil is activated. We call this SmartFocusTM TMS.
To be an effective therapy, TMS needs to reach the part of patient’s brain closely involved in emotion and mood. It’s quite small. We know it by the name the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) and believe it is one of the most inter-connected parts of the brain. We can’t see it. In fact, no-one can, unless we have a brain scan.
TMS used without image-based navigation simply estimates a spot for stimulation. We believe it is important that TMS targets the right location in patient’s brain – otherwise we may not get the benefit patients truly need. So, we use the latest science – 3D brain imaging and proven navigation of the TMS. We think focusing on patient as an individual is smart, so we are calling our solution to personalize depression therapy SmartFocusTM TMS.
Now there is a way to get the most out of TMS treatment. Our unique SmartFocusTM TMS uses the science of electricity to help the brain heal itself. Every treatment is personalized to patient’s brain anatomy and alertness level, to offer patients:
- A measured and individualized dose of TMS
- A level of accuracy demanded by brain surgeons
- Treatment sessions personalized for patient and patient’s brain
- Assurance that patient receives his/her prescribed dose
- Unsurpassed safety and comfort
To benefit from E-field navigation, the SmartFocusTM TMS system only requires a short, one-time setup process. The system then guides a trained operator to deliver a series of personalized therapy sessions, reliably and precisely-all in just a few steps.
~
How SmartFocusTM TMS works?
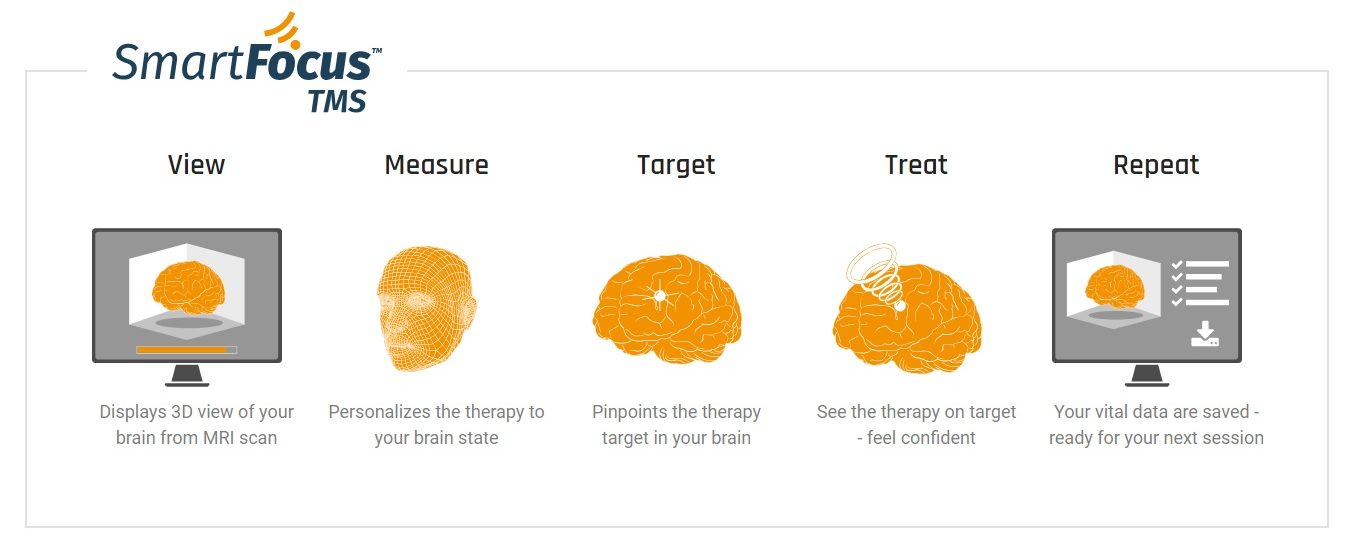
Using an MRI head scan, Nexstim SmartFocus™ TMS builds a 3D rendering of the patient’s brain. By “peeling” to a depth of 2-3 cm (1 in), you will be able to see the patient’s actual cortical anatomy in detail. Using a published, science-based algorithm*, instead of the 5 cm rule-of-thumb technique, you can then determine the precise location of the left DLPFC target within the individual’s brain anatomy.
The Nexstim system displays the location and the orientation of the maximum induced E-field overlaid in the cortical anatomy. As you move, turn or tilt the coil-even slightly-the system screen displays the updated E-field strength and location, all in real-time.
Accurately marking the left DLPFC, just once, gives your patient the benefit of receiving therapy to the same, precise location over the entire course of their treatment-and later, visit after visit.
**Mylius V, Ayache SS et al., Neuroimage. 2013 Sep; 78:224-32
~
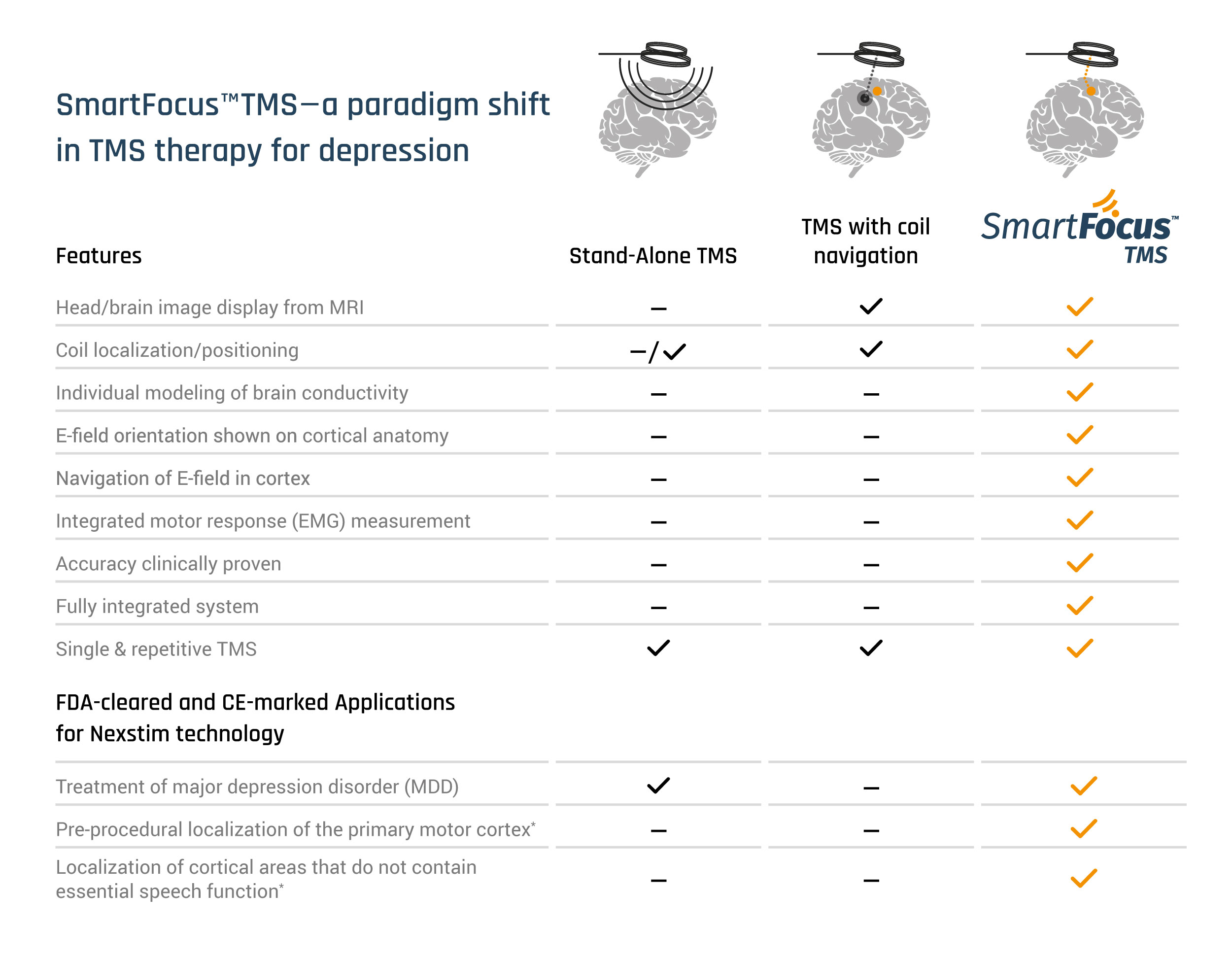
Why SmartFocusTM TMS is different?
SmartFocusTM is truly personalised TMS therapy for each individual patient. Here we tell why SmartFocusTM is different than the others.
- SmartFocusTM TMS by Nexstim is navigated TMS
In depression, activity of the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) is reduced (e.g. George et al, 1995) Stimulation of this area by rTMS increases the activity.
TMS with navigation enables accurate targeting of DLPFC. Without neuronavigation, the correct area is optimally targeted only in approximately 30% of patients (e.g. Herwig et al, 2001).
- However, SmartFocusTM TMS is not like the others: it’s an E-field navigated TMS
When a TMS coil is activated, it produces a stimulating electric field (E-field) in the cortex. Researchers have shown that the location of this E-field in the cortex is dependent on both the conductivity, as well as the geometry, of the underlying brain tissues.
The shape of the human head and brain is far from spherical and calculating the location of the E-field requires sophisticated modeling of tissue geometry. Nexstim uses an algorithm based on mathematically modeling the human brain as over 40,000 spheres—taking into account the locally fitted conductivity model on the induced E-field.
The unique multi-sphere model used by Nexstim has been scientifically-validated to accurately determine the location and orientation of the maximum induced E-field in the brain.**
The user of a SmartFocusTM System can be confident that whatever location, angle or tilt of the TMS coil relative to the head, a stimulus with the calculated and displayed E-field will be reliably delivered to the targeted cortical location.
With SmartFocusTM TMS you are not only navigating the coil, you navigate the e-field. That means, you can navigate the stimulation to the right spot in every patient’s unique brain.
- With SmartFocusTM you personalise the stimulation level
With SmartFocusTM TMS you also personalise the stimulation level of the TMS therapy.
First the motor strip on each patient’s brain is identified. After this, TMS is applied to the hand motor representation area, the “hand knob” with varying intensities to quantify the patient’s resting motor threshold, RMT. With that information SmartFocusTM uses an algorithm that eases the calculation of the correct TMS stimulation intensity for the patient.
- In addition, it is all visualised in the real-time
SmartFocus™ TMS creates a 3D model of the patient’s brain from an MRI head scan. Everything can be then onwards be seen on the screen: motor mapping area, the right spot on DLPFC, the stimulation level. And the most important part: As the operator moves, turns or tilts the coil—even slightly—the system shows the updated location, orientation and E-field data in real time.
** Krieg S (Ed.), Navigated Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Neurosurgery, Springer International Publishing, 2017
~
Personalizing TMS therapy for the individual patient – the science behind SmartFocusTM TMS
As the world’s leading company combining TMS with 3D imaging, Nexstim’s solution enables personalized TMS treatment with unsurpassed accuracy and precision.
- Targeting the left DLPFC
TMS is targeted to a region of the brain called the left DLPFC (dorso-lateral pre-frontal cortex) which is at a depth easily accessible by the normal strength of magnetic field emitted by TMS coils. PET imaging studies in patients diagnosed with MDD have shown lower metabolism, compared to controls, in their left DLPFC regions, which supports the concept of using TMS as a therapy to increase the excitability of the left DLPFC.
The left DLPFC has been validated as an efficacious target in several large, randomized controlled trials. The effects of TMS treatment have been shown to be dependent on the left DLPFC region receiving a sufficient “dose” of E-field each session and the sessions being repeated almost daily over many weeks. The observed effects of TMS suggest that the part of the mechanism behind TMS is neuroplasticity, the brain responding to the TMS treatment by “re-wiring” its own circuits.
Researchers have shown that the location of the E-field in the brain is dependent on both the conductivity as well as the geometry of the underlying tissues. Calculating the E-field location requires sophisticated modeling of tissue geometry. Nexstim uses an algorithm based on mathematically modeling the human brain as over 40,000 spheres—taking into account the locally fitted conductivity model on the induced E-field.
The Nexstim multi-sphere model of the brain has been scientifically-validated to accurately determine the location and orientation of the maximum induced E-field—and is the foundation for the FDA-clearance of our technology for pre-procedural planning, used in neurosurgery.**
** Krieg S (Ed.), Navigated Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Neurosurgery, Springer International Publishing, 2017
- Personalising the stimulation level for the individual patient
The effects of stimulation are always dependent on the intrinsic excitability state of the patient’s brain and cortex. This state is unique for each patient but can easily be measured by TMS.
Once the motor strip has been identified, TMS is applied to the hand motor representation area, the “hand knob” with varying intensities to quantify the patient’s resting motor threshold, RMT. A patient’s RMT is defined as the minimum stimulation intensity capable of generating a MEP in 50% of given stimuli. Nexstim systems use an algorithm to ease the calculation.
It is important to carefully map for the optimal hand knob location using all the dimensions available for moving the coil, especially rotation. The goal of this mapping is to locate the site most sensitive to stimulation, otherwise the patient’s true resting-state cortical excitability cannot be determined. If the patient’s motor threshold calculation is based on measurement at an erroneous location, there is the subsequent danger of over-stimulating the cortex in therapy, as well as causing the patient unnecessary discomfort or pain.
rTMS therapy for depression is normally given at 120% of RMT. Cortical motor mapping can normally be performed at 110% of RMT, or higher.
- Level of accuracy demanded by brain surgeons
The accuracy of Nexstim’s TMS solution is validated by neurosurgeons. In neurosurgery, the “gold-standard” technique for cortex localization is direct electrocortical stimulation (DES or DCS). DES is a highly invasive procedure. The term “direct” refers to the fact that there is a direct cause-and-effect relationship between the input (E-field) and the output (for example quantitative measurement of muscle EMG amplitude).
TMS is the only non-invasive modality that is fully analogous to DES in that both techniques are based on electrical stimulation of a small volume of brain tissue and the direct measurement of the induced effects. The clinical utility of DES is perceived to be very high by neurosurgeons and, although its absolute accuracy is impossible to verify. The accuracy of Nexstim’s TMS solution has been validated by comparing the concordance of pre-operative NBS mapping results with the results of subsequent intraoperative DES in the same patients.
There is little data on the accuracy of coil-navigated, “line-navigated”, TMS. The largest published study comparing line-navigated TMS to E-field-navigated TMS found significantly different results from the two methods, with only a partial overlap of the derived motor maps and, in several patients, line-navigated TMS located the targeted motor hotspot in different gyri compared to Nexstim’s solution.***
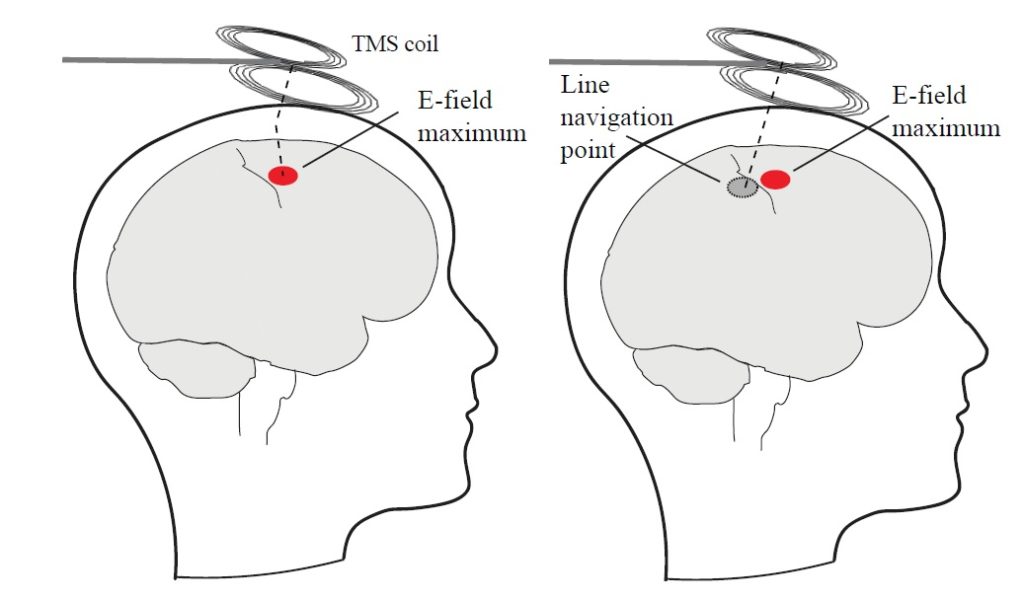
The user of a Nexstim’s System can be confident that whatever location, angle or tilt of the TMS coil relative to the head, a stimulus with the calculated and displayed E-field will be reliably delivered to the targeted cortical location.
***Sollmann N Comparison between electric-field-navigated and line-navigated TMS for cortical motor mapping in patients with brain tumors. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2016 Dec;158(12):2277-2289.
~
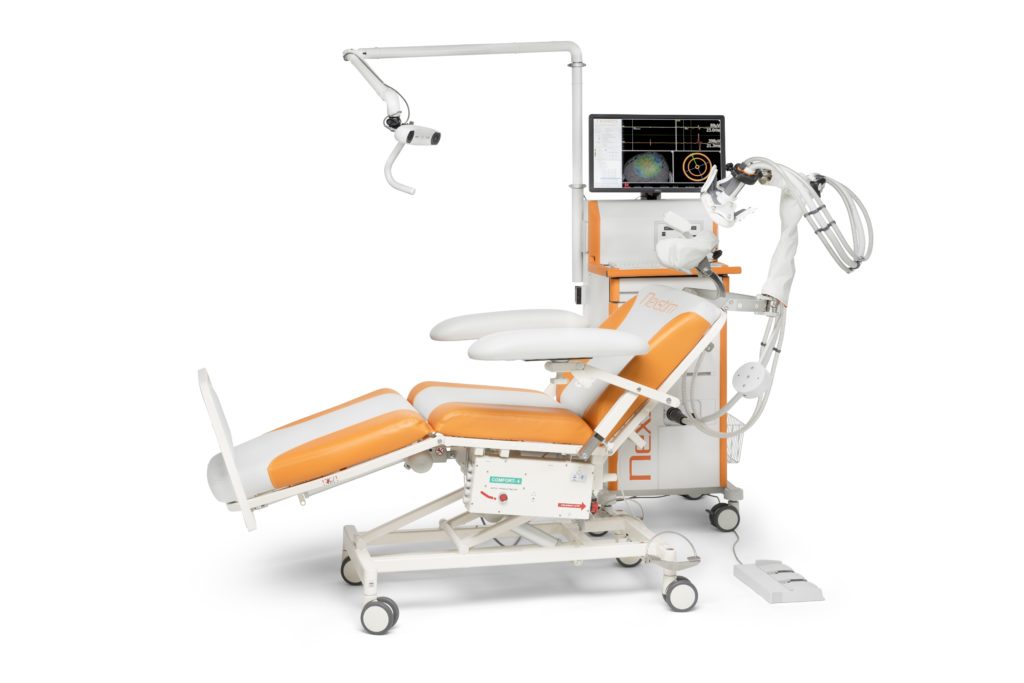
Nexstim NBT® System components
The NBT System 2 comprises the following components:
- Mobile Nexstim cart
- Nexstim TMS stimulator
- Nexstim stimulation coil
- Stereotactic camera (arm-mounted tracking unit)
- 6-channel Nexstim EMG
- Computer system with display, PC and NBT software
- Three-pedal foot switch
- Nexstim cooling unit
- Electronically adjustable patient chair with coil positioning holder.
- Tracking tools: NBT head tracker, coil tracker and digitizing pen
~
Indications for use
FDA: Nexstim Navigated Brain Therapy (NBT) System 2 is indicated for the treatment of Major Depressive Disorder in adult patients who have failed to achieve satisfactory improvement from prior antidepressant medication in the current episode.
CE mark: Nexstim Navigated Brain Therapy System for depression is intended to be used for treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) by targeting and delivering non-invasive repetitive TMS stimulation to the patient’s dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Nexstim NBT System is indicated for MRI-guided and electric field (or E-field) navigated, noninvasive, repetitive TMS stimulation (rTMS) of the motor cortex as therapy to alleviate chronic unilateral neuropathic pain in adult patients. Nexstim NBT System is indicated for MRI-guided and electric field (or E-field) navigated, noninvasive, repetitive TMS stimulation (rTMS) of the motor cortex as an adjunct therapy to rehabilitation of upper extremity motor function.
To find out where to get SmartFocusTM TMS therapy in Hong Kong, please click here.
To request for more information or a presentation, please click here.
